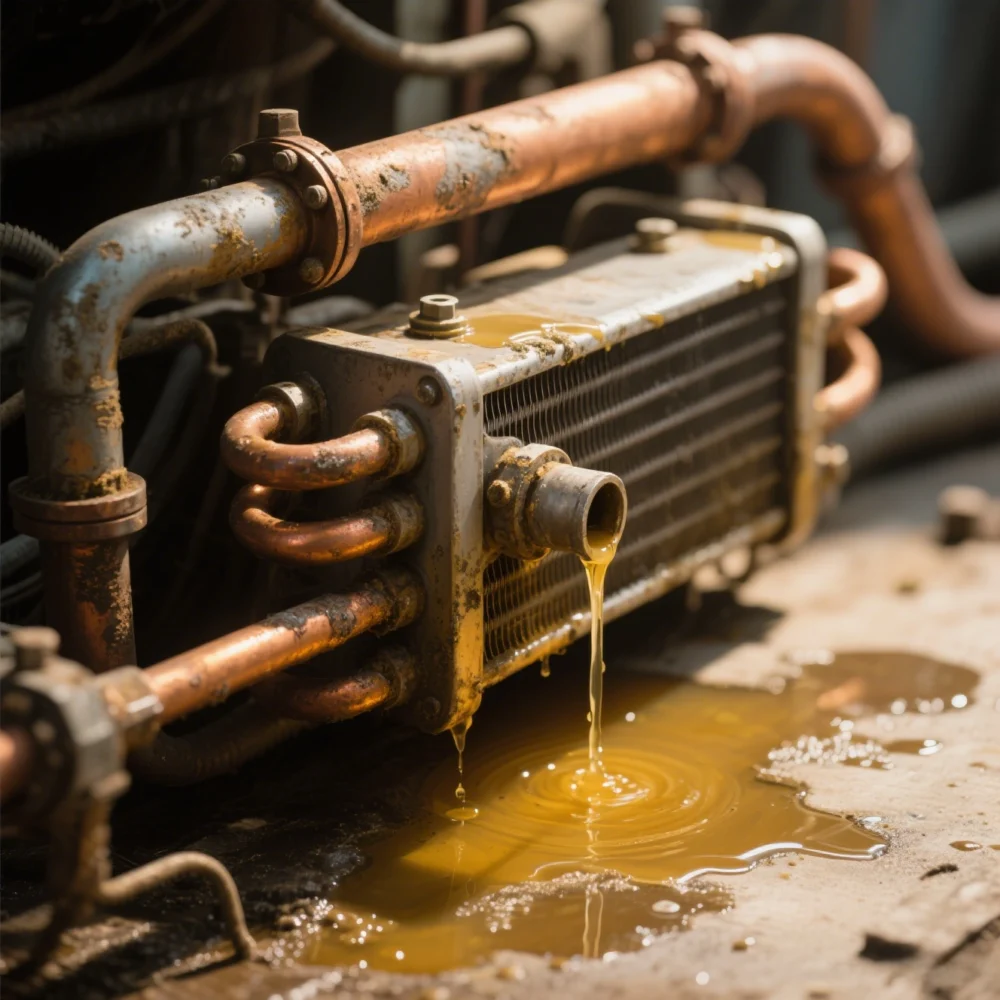
1. Cooler is corroded
The main causes of corrosion are materials, environment (water quality, gas) and electrochemical reaction.

Selecting corrosion-resistant materials is an important measure to prevent corrosion. For example, the fixed hole plate, the moving hole plate and the cooling copper pipe mouth often have serious corrosion. The solution is to improve the cooling water quality and to select cooling pipes made of aluminum alloy and diamond alloy.
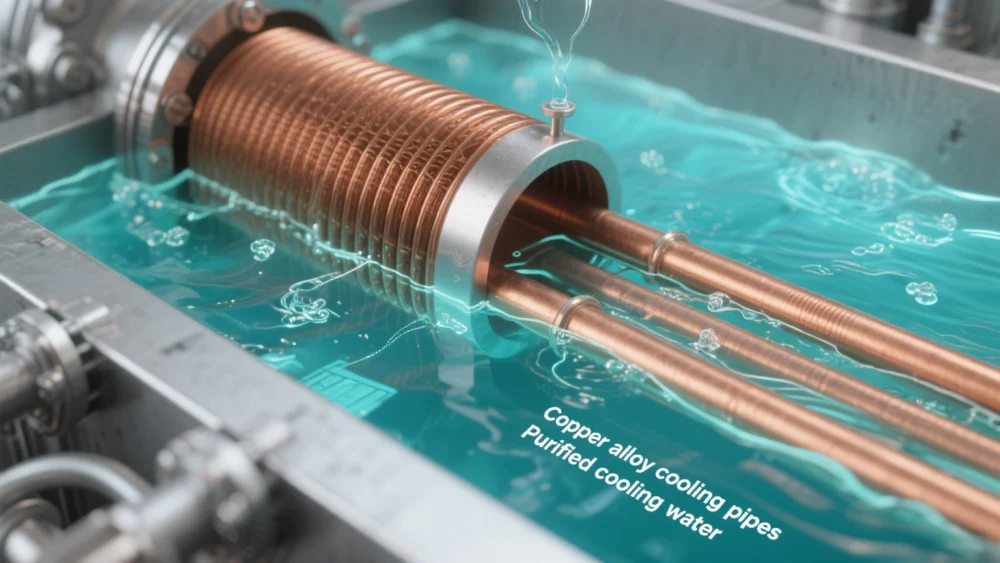
In addition, the environment of the cooler includes dissolved oxygen, water quality (pH value) of cooling water, temperature, flow rate and foreign matter. The more oxygen dissolved in the water, the more intense the corrosion reaction; in the acidic range, the lower the pH value, the more active the corrosion reaction and the more serious the corrosion; in the alkaline range, for amphoteric metals such as aluminum, the possibility of corrosion increases with the increase of pH value; the increase of flow rate increases the oxygen supply to the metal surface on the one hand, and on the other hand, the excessive flow rate generates turbulent vortex, which will cause cavitation corrosion; in addition, sand and gravel in the water, tiny shellfish bacteria attached to the cooling pipe, often cause local erosion.

In addition, the presence of chloride ions increases the conductivity of the liquid used, which increases the corrosion caused by electrochemical reactions. In particular, chloride ions adsorbed on stainless steel and aluminum alloys will also partially damage the protective film, causing pitting and stress corrosion. Generally, corrosion increases with increasing temperature.
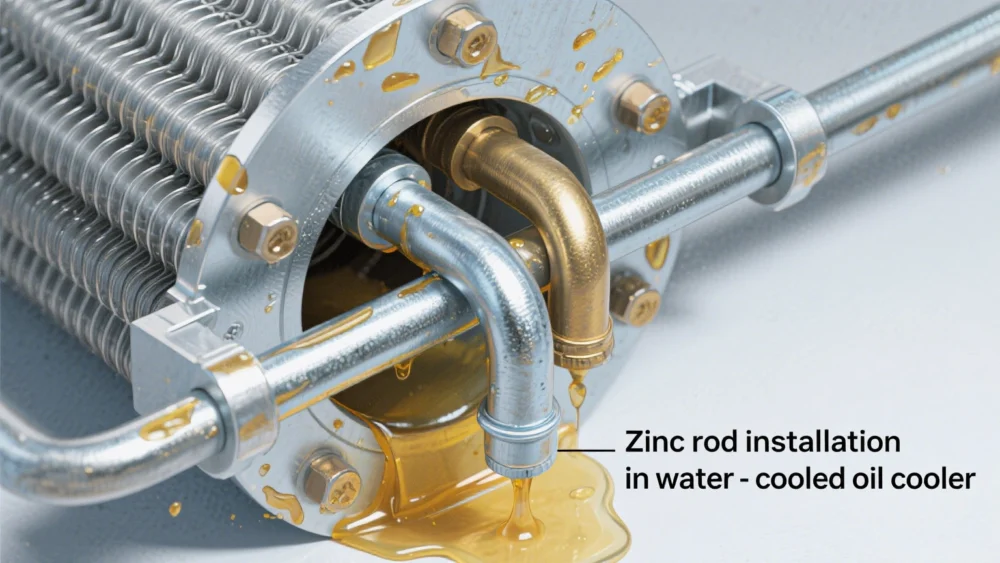
To prevent corrosion, attention should be paid to cooler material selection and water quality treatment. The former is often difficult to change, but users can find ways to deal with the latter. The zinc rods installed in water-cooled oil coolers to prevent electrolytic corrosion should be checked and replaced in a timely manner.
2. Decreased cooling performance
The main reason is blockage and sediments retained on the cooling pipe wall, forming hard lumps and pipe scale, which reduces the heat dissipation and heat exchange function. In addition, insufficient cooling water and air accumulation in the water-oil chamber of the cooler will also cause a decrease in heat dissipation and cooling performance. The solution is to first adopt a structure that is difficult to block and easy to clean in design; use mechanical methods (such as brushes, pressure, water, steam, etc.) or chemical methods such as cleaning agents for cleaning when necessary; increase the water intake or use water with lower temperature for cooling; unscrew the screw plug to exhaust; clean the scale on the inside and outside.

3. Damage
Due to the temperature difference between the two fluids, the oil cooler material is affected by thermal expansion, generating thermal stress, or the inflow oil pressure is too high; it may cause the relevant parts to break. In addition, in cold areas or in winter, when the machine is shut down at night, the ice in the pipe will expand and burst the cooling water pipe. Therefore, it is necessary to try to use materials that are not easily affected by thermal expansion and use deformation compensation structures such as floating heads.
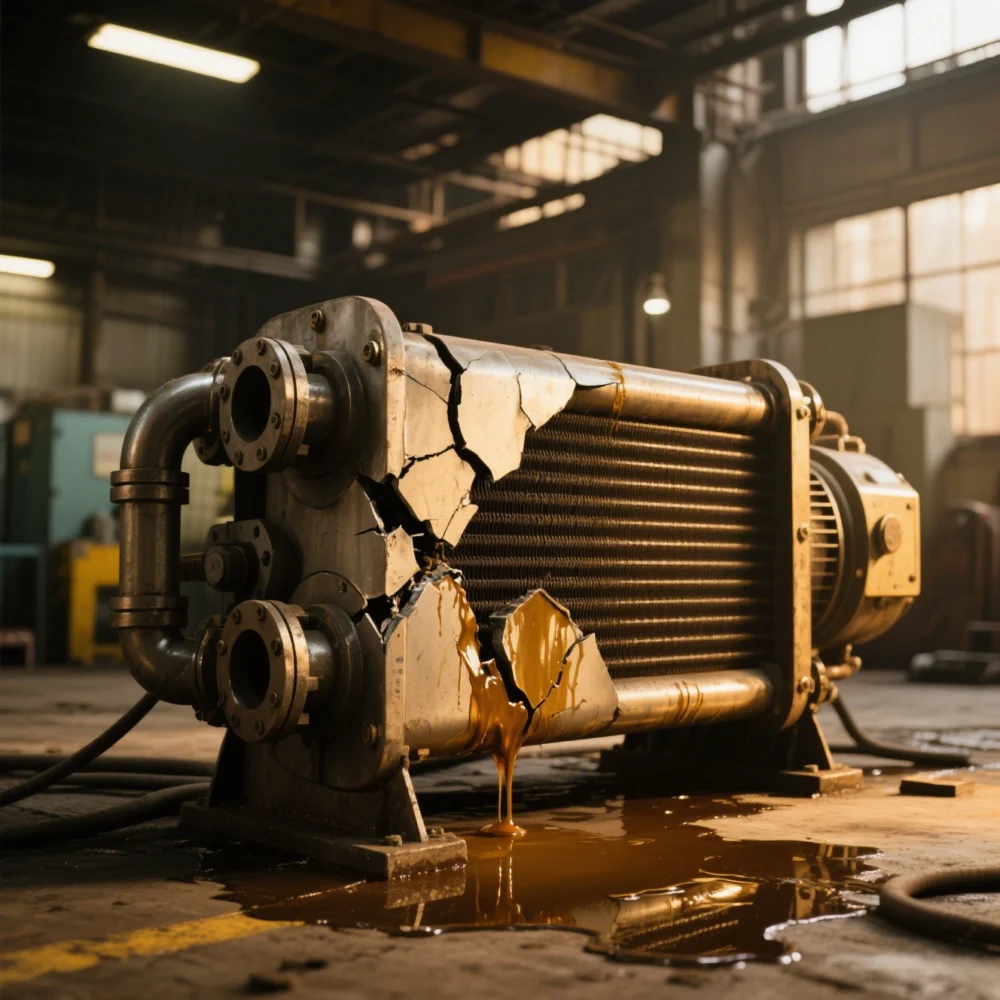

4. Oil leakage and water leakage
Water leakage and oil leakage often occur at the joint surface between the end cover and the cylinder of the oil cooler, or due to poor welding, rupture of the cooling water pipe, etc. At this time, according to the situation, measures such as replacing the seal and repair welding can be taken to solve it. When replacing the seal, clean the joint surface and apply a layer of adhesive.
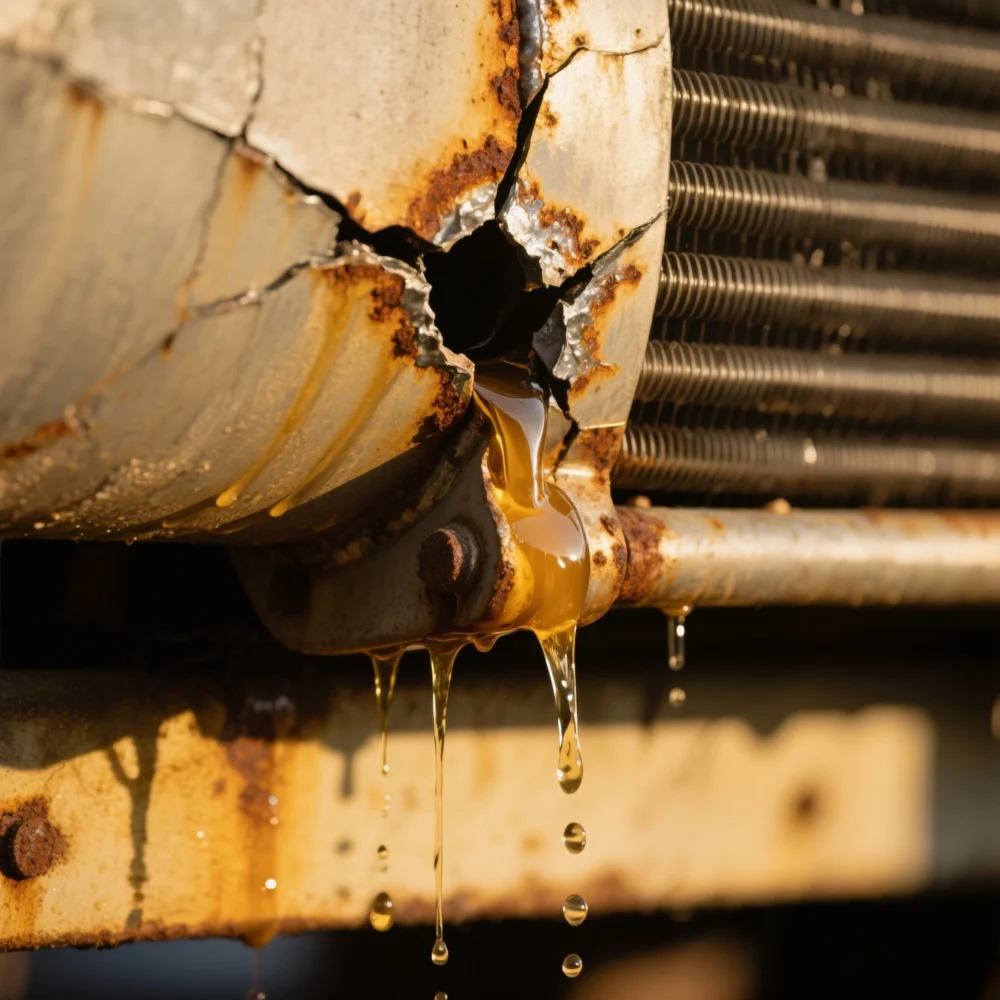

5. Overcooling
The overflow volume of some cooling circuit overflow valves changes with the load flow of the system, so the heat generation will also change, sometimes resulting in overcooling and waste. In order to ensure that the system has a suitable oil temperature, a temperature control system that can automatically adjust the cooling water volume can be used. If the oil temperature is lower than normal, stop the cooler, or even turn on the heater.
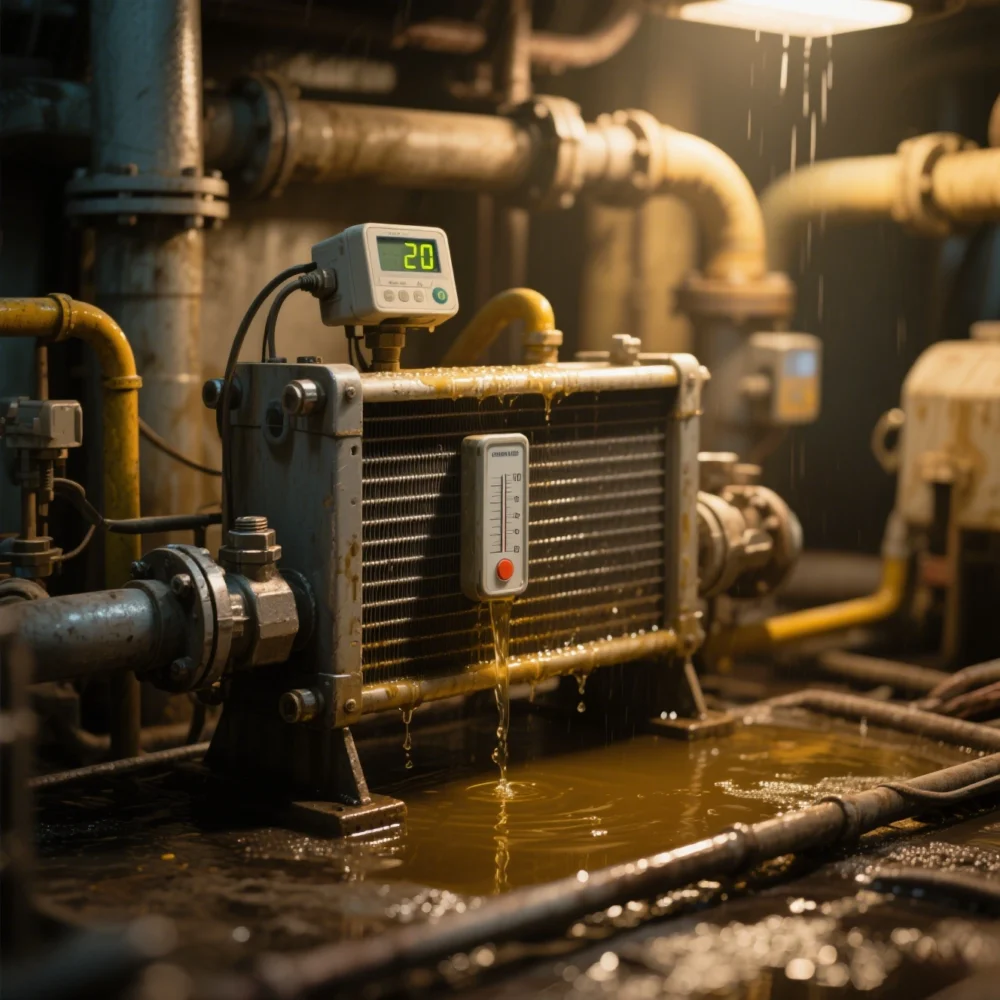

6.Low efficiency
Poor cooling water quality (hard water), scaling in the cooling copper tube, resulting in reduced cooling efficiency.
At this time, the oil cooler can be cleaned as follows:
①Use a hose to draw clean water to quickly rinse the return cover, the inner wall of the rear cover and the inner surface of the cooling tube, and use a cleaning rod to wash at the same time, and finally blow dry;
②Rinse with trichloroethylene solution to circulate the cleaning liquid in the cooler. The cleaning pressure is about 0.5MPa, and the cleaning time depends on the solution. Finally, introduce clean water into the tube until clean water flows out.
③Pour carbon tetrachloride solution into the cooler. After 15~20min, it depends on the color of the solution. If it is turbid, replace it with a new solution and soak it again until the outflowing solution is almost the same as the clean solution, and then rinse it with clean water. This operation should be performed in a ventilated environment to avoid poisoning.

