What is the internal principle and structure of the axial piston pump, and how does it suck and discharge oil?
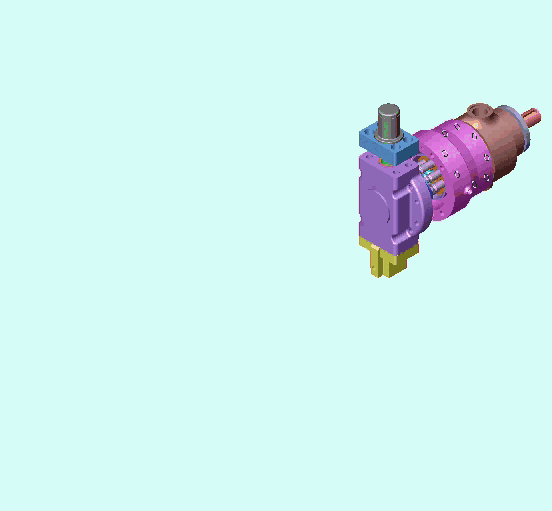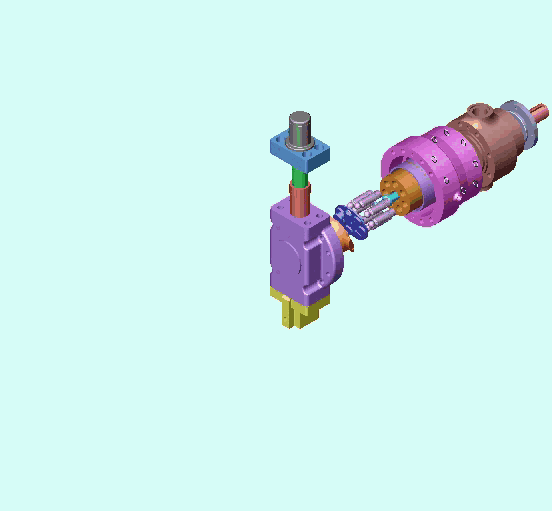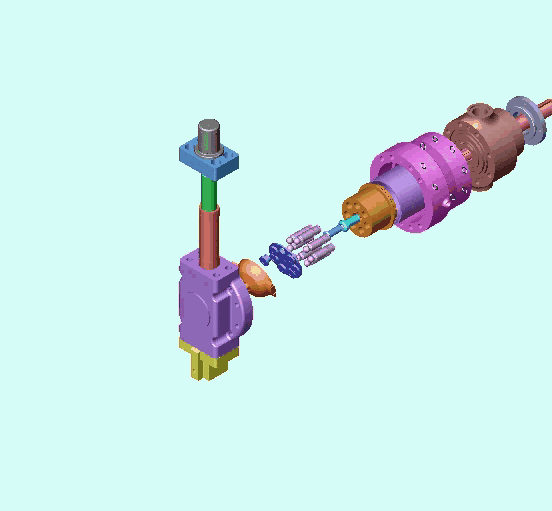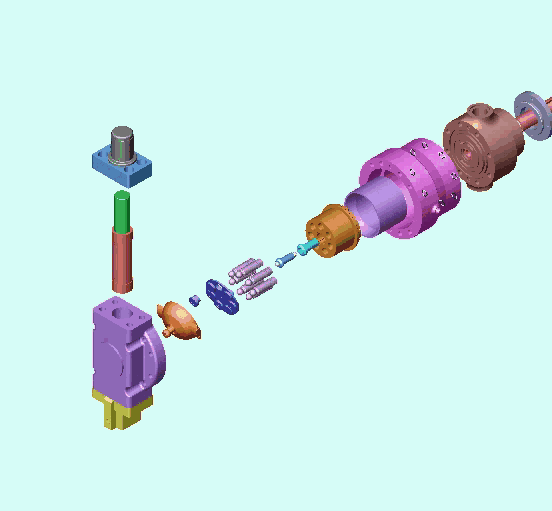
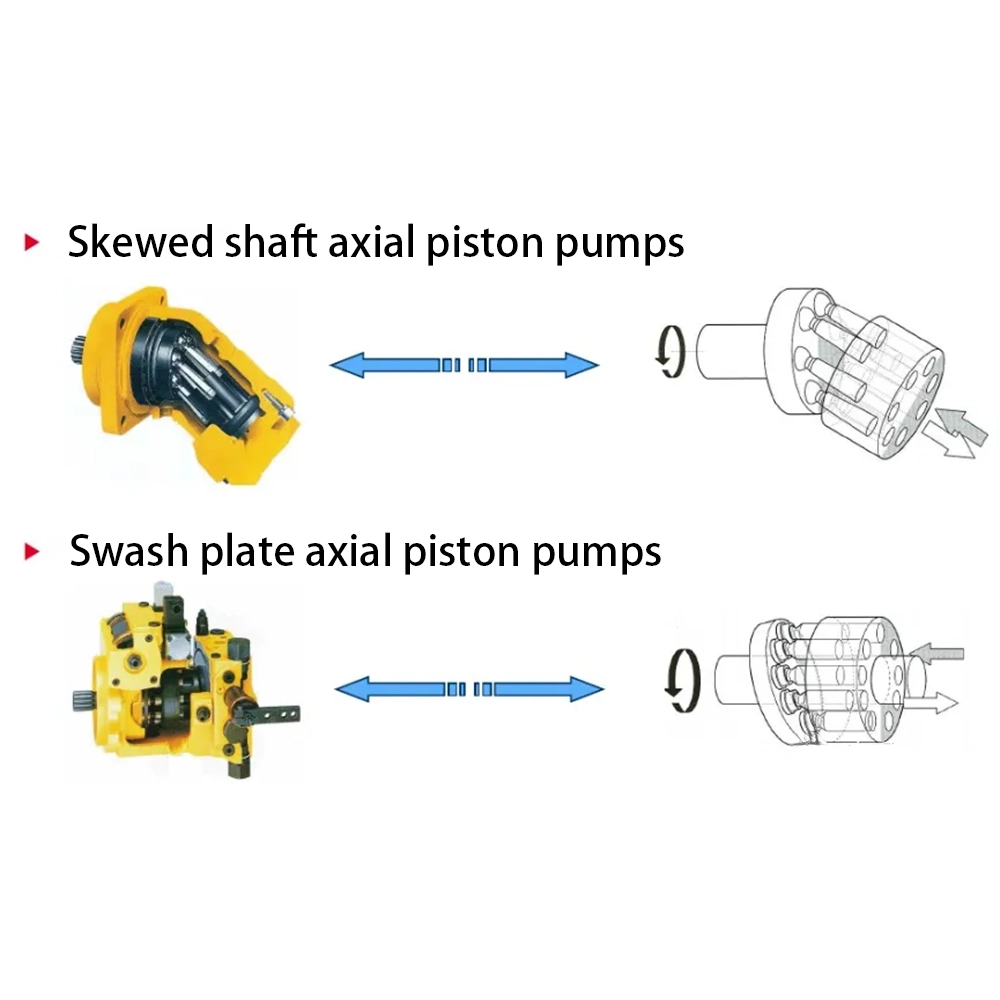
1、Classification of piston pumps (motors):
The types of axial piston pumps are the same as axial piston motors and are also divided into two categories: straight-axis axial piston pumps and inclined-axis axial piston pumps.
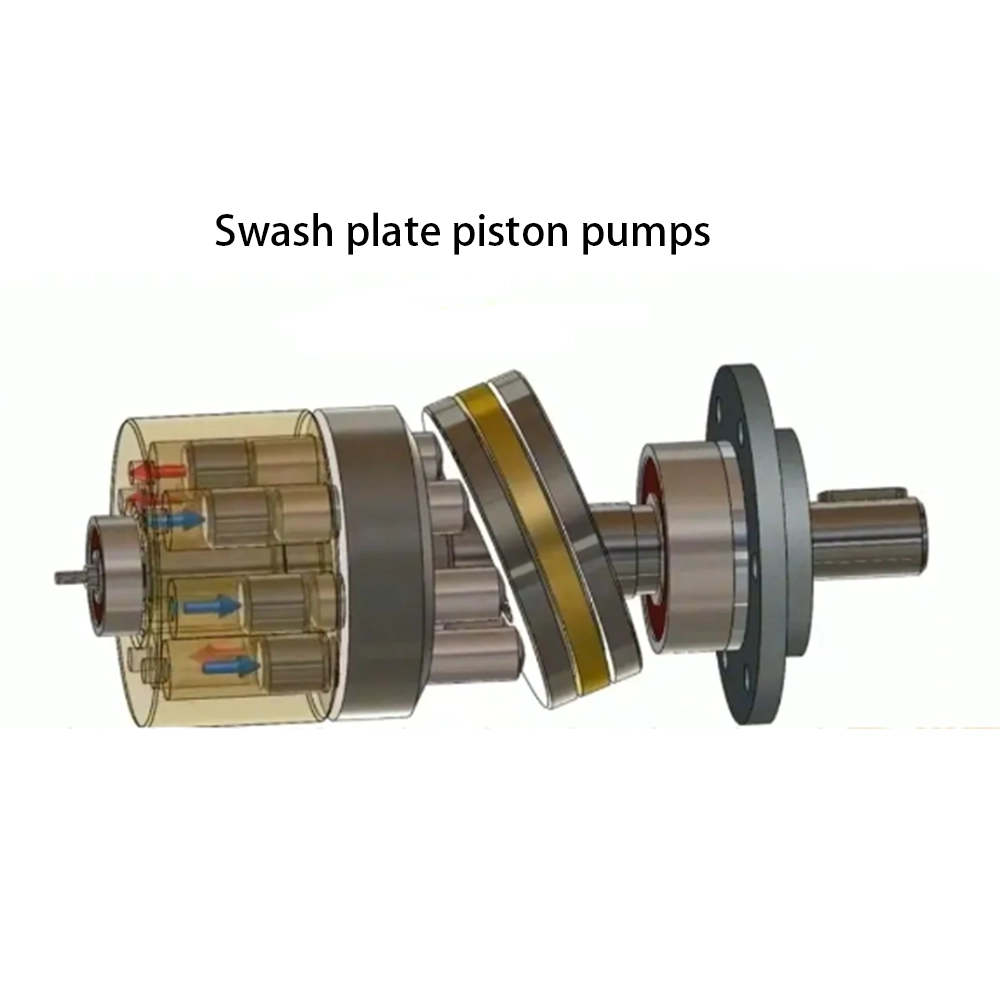
Swash plate plunger pump: every rotation of the cylinder body, each plunger reciprocates once to complete a suction and discharge action. Changing the inclination angle of the swash plate can change the effective change of the sealing working volume and realize the variable of the pump.

The drive shaft of a swash-axis axial piston pump is inclined at an angle to the cylinder axis, hence the name swash-axis pump.
Compared with swash plate axial piston pumps, it has the following characteristics.
(1) The radial force on the plunger in swashplate axial piston pump is very small, so the angle between the drive shaft and the cylinder axis is allowed to be large, and thus the pump displacement is larger.
(2) The cylinder is subjected to a small overturning moment, the end face of the cylinder and the flow distribution disk fit uniformly; the leakage loss is small, high volumetric efficiency; friction loss is small, high mechanical efficiency.
(3) Sturdy structure, good impact resistance.
(4) Because the drive shaft of the inclined shaft pump must withstand considerable axial force and radial force, it needs to adopt thrust bearing with large bearing capacity.
(5) The total efficiency of the swash-axis pump is slightly higher than that of the swash plate pump. The inertia of the moving parts is large, and the dynamic response is slow.
2. Structure and working principle of plunger pump (motor):
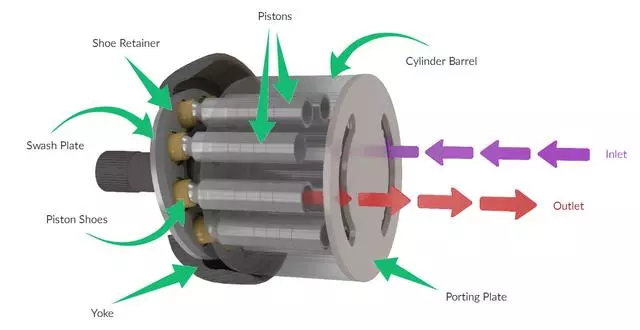
The following picture shows the core components of the axial piston pump and the oil inlet and outlet conditions.
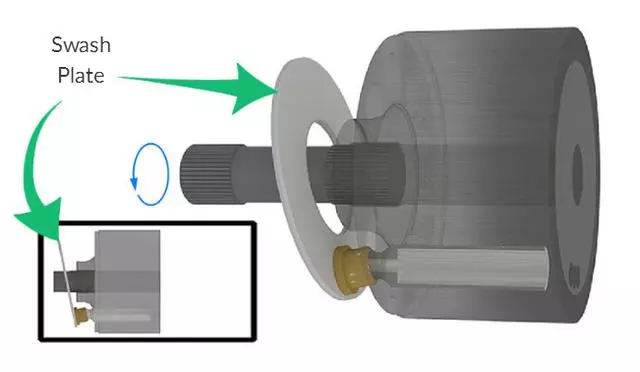
The oil suction and discharge process of a single plunger is briefly introduced. The following figure shows that the single plunger begins to enter the critical state of preparing to suck oil when it is at the lowest end.
When the plunger rotates to the top position, the plunger hole is just filled with oil and is about to be discharged. This is the critical state of oil discharge.
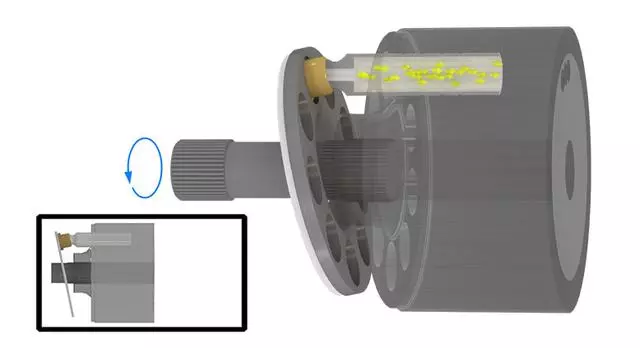
The following animated picture shows a complete oil suction and discharge process. If the cylinder body rotates continuously, the plunger will also continuously suck and discharge oil. This is the working principle of the axial piston pump.
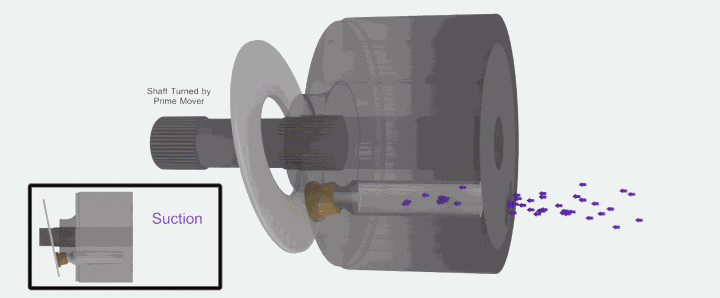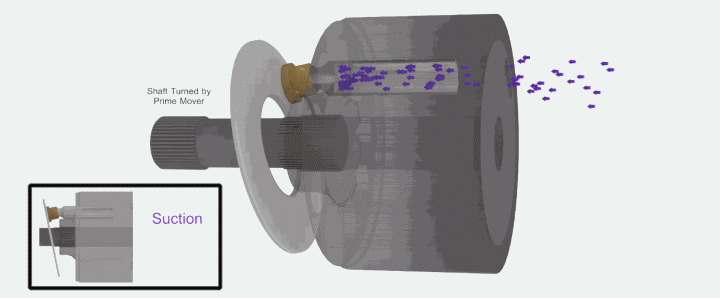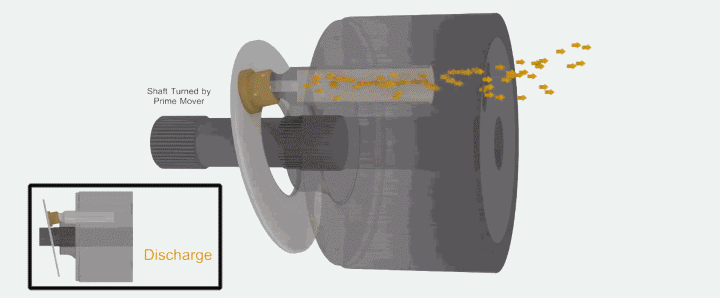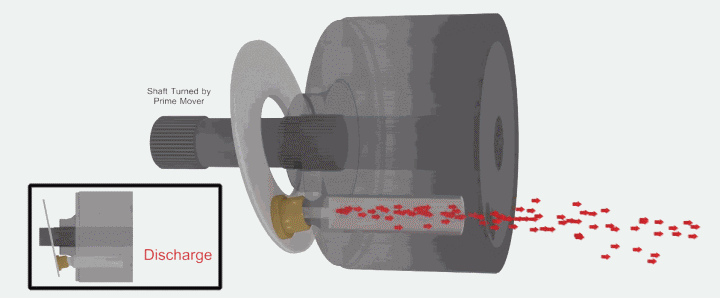
It’s easy to understand when you look at it again in the context of the overall structure
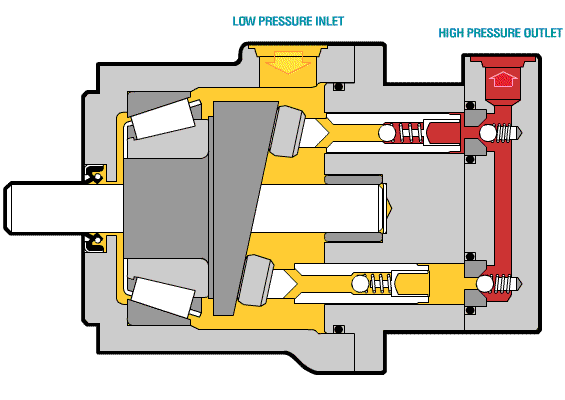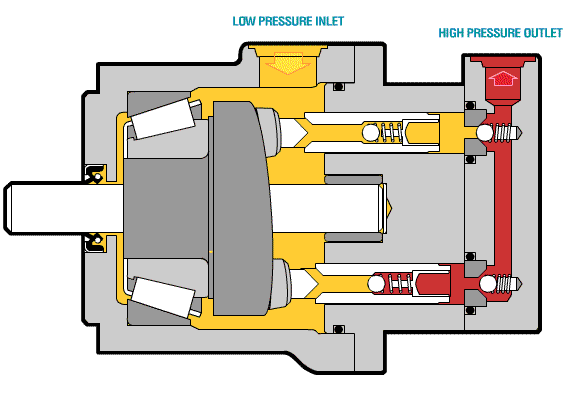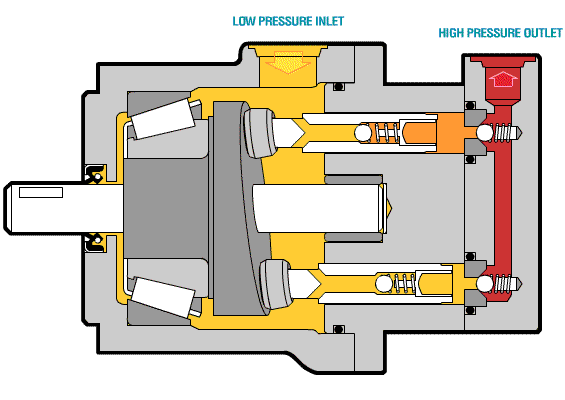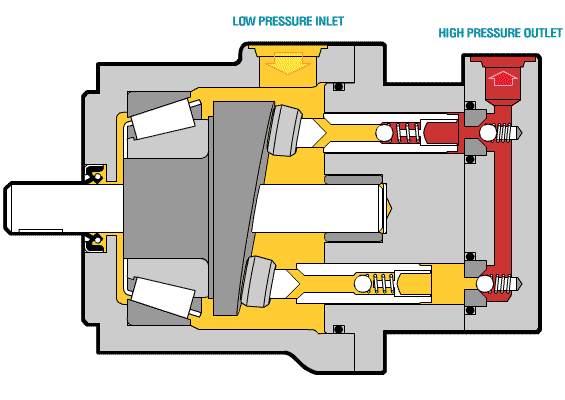
Above is a moving picture of the piston pump, we can see the structure through the moving picture.
The following picture is from the introduction of Hytek piston pumps (motors)
After understanding the structure and principle of the piston pump, we look at the following moving picture, it is a hydraulic motor, or piston pump.

Some people say this is a hydraulic motor, others point out that it is a piston pump. The reason for the confusion, mainly because the structural form of the axial piston motor is basically the same as the axial piston pump. In principle, hydraulic motors and hydraulic pumps are reversible, if driven by an electric motor, the output is pressure energy (pressure and flow) which is a hydraulic pump; if the input pressure oil, the output is mechanical energy (torque and speed), it becomes a hydraulic motor. This is like the relationship between a generator and an electric motor.
