1.Selection and installation of hydraulic gear pumps
When selecting a hydraulic gear pump, it is necessary to make a judgment based on the properties of the liquid to be transported. At the same time, it is necessary to conduct a detailed inspection of the pump’s performance requirements and analyze its suction and discharge conditions, whether it is intermittent or continuous operation. Normally, the pump should operate at a working pressure and flow rate close to or in accordance with the manufacturer’s specified conditions. During the installation process, the following points need to be fully reviewed:
(1) The size, location and elevation of the foundation should strictly comply with the design specifications. The anchor bolts must be firmly fixed to the concrete foundation. The pump body should be kept intact without any defects or rust.
(2) According to the characteristics of the conveying medium, the materials of the main components, shaft seals and gaskets should be inspected when necessary.
(3) The installation and cleaning standards of all pipes and accessories connected to the pump body should comply with relevant national standards.
2. Specifications for use of hydraulic gear pumps
①The trial operation of the pump must meet the following conditions:
(1) The direction of the drive motor must be consistent with the direction of the pump.
(2) The direction of the pipeline pump and the coaxial pump must be verified to be correct.
(3) All fixed connections should be tightened reliably, and the type and quantity of lubricants for each lubrication point should follow the guidance of the equipment technical documents.
(4) Parts that require pre-lubrication must be handled in accordance with relevant regulations.
(5) All indicating instruments and safety protection devices should have sensitivity, accuracy and reliability.
(6) The rocker should move flexibly and without abnormal phenomena.
(7) High-temperature pumps must be preheated before trial operation, and the temperature rise must be stable. The temperature rise per hour should not exceed 50°C; the temperature difference between the pump surface and the process pipeline at the working medium inlet should not exceed 40°C.
(8) A connection device must be set to control the influence of temperature rise, and a bypass device must be installed to provide cooling water.

②When operating a hydraulic gear pump, the following precautions should be observed:
(1) Oil-free operation is strictly prohibited, and the displacement should not be reduced by adjusting the suction volume to avoid low-flow operation.
(2) The operation process should be closely monitored to prevent leakage of the stuffing box. When replacing the stuffing box, a new packing should be used.
(3) Ensure that the mechanical seal has sufficient flushing water flow and prevent excessive water supply to the water-cooled bearing.
(4) Avoid using too much lubricant.
(5) Be sure to check according to the recommended cycle and establish operation records, including operation time, packing adjustment and replacement, lubricant addition and other maintenance measures and time.
(6) Regularly measure and record the suction and discharge pressure, flow, input power, flushing fluid, bearing temperature and vibration of the hydraulic gear pump.
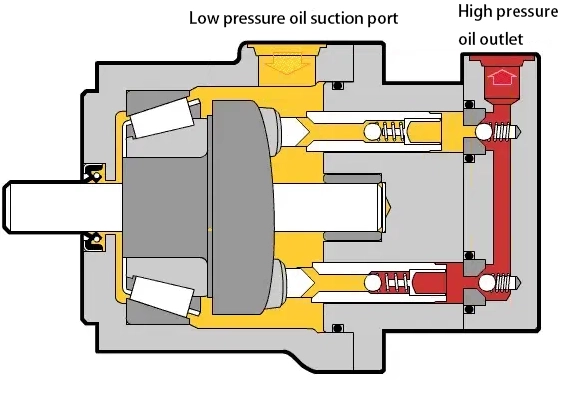
3. Maintenance and management of hydraulic gear pumps – analysis of mechanical seal failure
(1) Oil-free operation is strictly prohibited, and the displacement should not be reduced by adjusting the suction volume to avoid low-flow operation.
(2) The operation process should be closely monitored to prevent leakage of the stuffing box. When replacing the stuffing box, a new packing should be used.
(3) Ensure that the mechanical seal has sufficient flushing water flow and prevent excessive water supply to the water-cooled bearing.
(4) Avoid using too much lubricant.
(5) Be sure to check according to the recommended cycle and establish operation records, including operation time, packing adjustment and replacement, lubricant addition and other maintenance measures and time.
(6) Regularly measure and record the suction and discharge pressure, flow, input power, flushing fluid, bearing temperature and vibration of the hydraulic gear pump.
(7) In addition, if the filter screen of the seal flushing liquid is clogged, it will also lead to insufficient water flow and eventually cause the mechanical seal to fail.
(8) The gap between the slide groove and the end face on the sealing surface may also cause mechanical seal failure during bonding.
(9) The medium is unclean and contains tiny hard particles, causing it to slide at high speed on the sealing surface, scratching the end face and eventually leading to failure.
(10) The coaxiality of the pump transmission parts is poor, and the end face swings and rubs during operation, causing the moving ring to be non-concentric, thereby causing overheating and wear problems.
(11) Frequent changes in the hydraulic characteristics of the liquid medium will cause the pump to vibrate, causing the sealing surface to be misaligned and fail.
(12) Liquid corrosion to the sealing element, stress concentration, poor material coordination, erosion, incompatibility and deformation of auxiliary sealing O-rings, V-rings, and concave rings will all affect the integrity of the mechanical seal surface. The damage should be comprehensively analyzed to find the root cause, to ensure the long-term stable operation of the mechanical seal.

4. Operation requirements after shutdown
(1) After the hydraulic gear pump is shut down, the pump inlet valve should be closed immediately, and the valves of the auxiliary system should be closed in sequence after the pump cools down.
(2) For high-temperature pumps, the shutdown process should follow the provisions of the equipment technical documents. After shutdown, turn half a turn every 20-30 minutes until the pump body cools down to 50°C.
(3) When the low-temperature pump is shut down, if there is no special requirement, ensure that the pump is always full of liquid and keep the suction valve and discharge valve open; for low-temperature pumps with double mechanical seals, the liquid pressure in the liquid level controller and pump sealing chamber must be maintained.
(4) For media that are easy to crystallize, solidify or precipitate, the pump and pipeline should be cleaned with water or other media in time after shutdown to prevent blockage.
(5) Drain the accumulated liquid in the pump to avoid rust and freezing.

5. Storage requirements
(1) The unmounted pump body should be coated with rust inhibitor on the unpainted surface, and the oil in the bearing should be kept sufficient. For bearings lubricated with grease, ensure that only a single type of grease is used to avoid mixing.
(2) In a short period of time, use pump cleaning fluid to flush the suction pipe, discharge pipe, pump casing and impeller, and ensure that the flushing liquid in the pump casing, suction pipe and discharge pipe is emptied.
(3) Empty the oil in the bearing box and add fresh and clean oil, then thoroughly clean the grease before adding new grease.
(4) Pay attention to closing the suction and discharge ports, store the pump body in a clean and dry environment, protect the motor winding from moisture, and spray rust and corrosion inhibitor on the inside of the pump casing.
(5) Turn the pump shaft every month to prevent freezing and ensure that the bearings are lubricated.